Gouldian Finches or Rainbow Finches
Gouldian Finches (Lady Gould) or Rainbow Finches
The Gouldian Finches (Erythrura gouldiae) are also known as the Painted Finches, Purple-breasted Finches, Rainbow Finches, Gould’s Finches, or Lady Gouldian Finches.
They were named for Elizabeth Gould, the wife of the British ornithological artist John Gould.
Distribution / Habitat
These stunning little finches are native to northern Australia, with scattered records from the Cape York Peninsula through north-west Queensland and the Northern Territory to the Kimberley region of Western Australia.
The birds are nomadic within a relatively small area of approximately 40 sq kilometers and only move when water or food becomes scarce.
In the wild, the Gouldians frequently gather in flocks – probably to protect against predation. These flocks may consist of up to 1000–2000 individuals.
During the breeding season, they are usually found on rough scree slopes where vegetation is sparse. In the dry season, they are more nomadic and will move to wherever there is food and water.
They are very popular in captivity, but they are endangered species in their natural habitat – with less than 2,500 of them remaining.
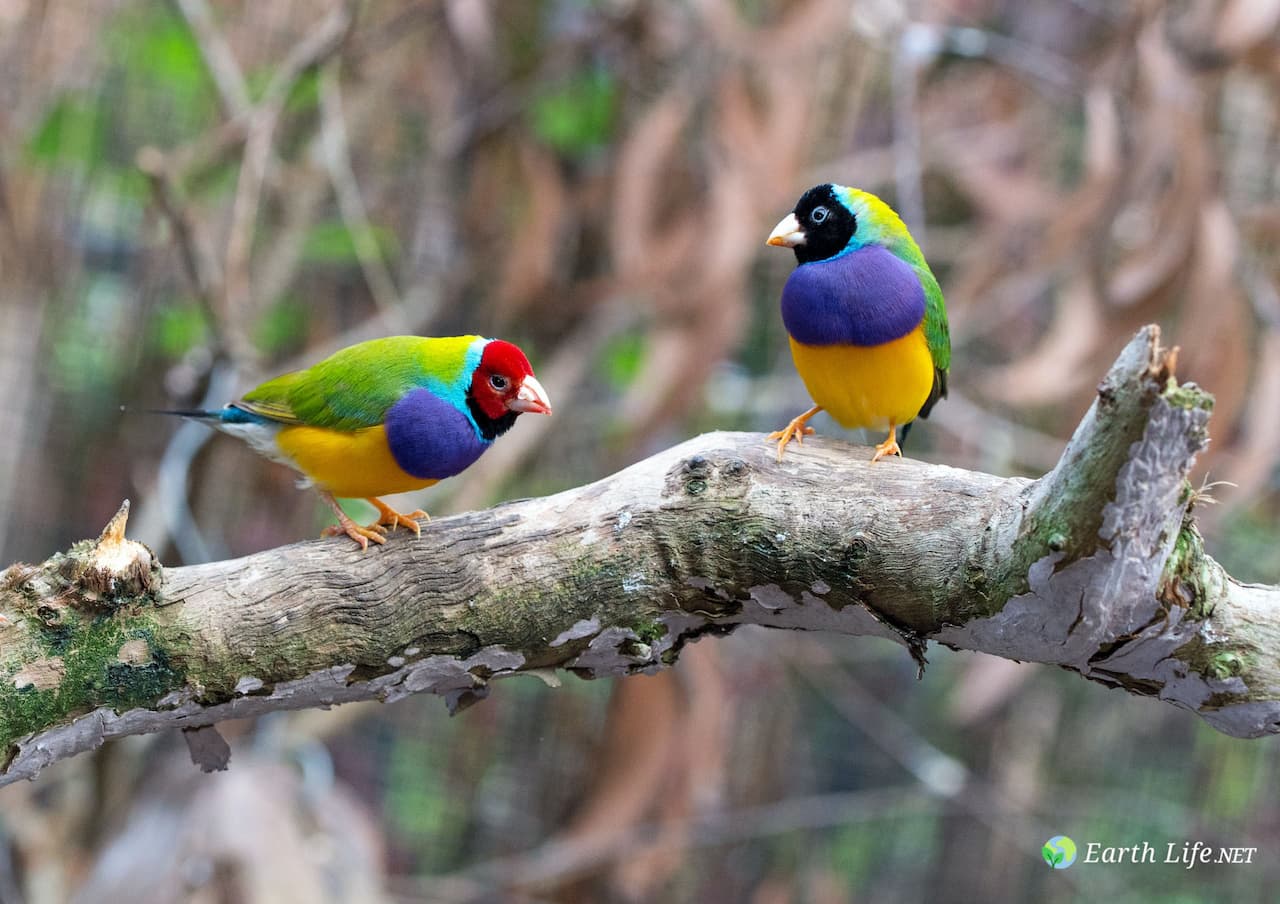

Description
Size
Gouldian Finches measure about 4.7 – 5.9 inches (12 – 15 cm) in length (including the tail) and weigh about 0.49 – 0.53 oz (14 – 15 g).
Plumage Details / Adults
Both males and females are brightly colored with black, green, yellow, red, and other colors.
Gouldian Finches’ heads may be red, black, or yellow. People used to think there were three different kinds of finches, but now it is known that they are color variants that exist in the wild.
Selective breeding has also developed mutations (blue, yellow, and silver instead of green back) in body and chest color.
Other Physical Details
The beak is flesh-colored overall, however, once the adults are in breeding condition, their beak tips turn either reddish, orangish, or blackish.
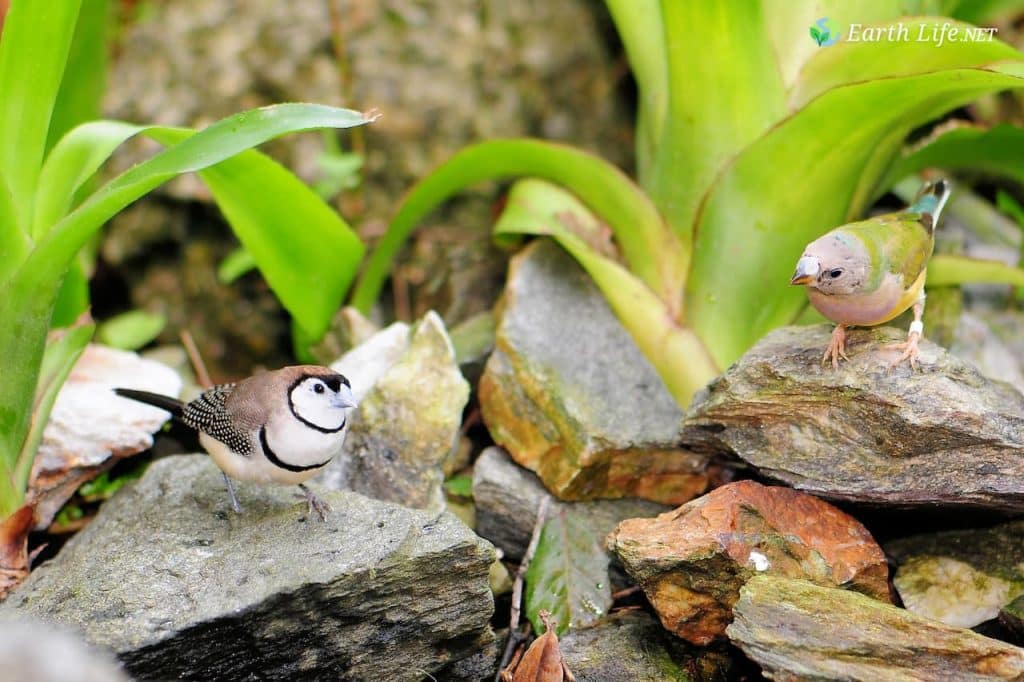

Gender ID
The females tend to be less brightly colored. One major difference between the sexes is that the male’s chest is purple, while the female’s is a lighter mauve color.
Juvenile Description
Juvenile birds have distinctive colors. Their heads, sides, and necks are grey, and their backs, wings, and tail feathers are olive green. Their undersides are pale brown. Beaks are blackish with a reddish tip. Their legs and feet are light brown.
Newly hatched Gouldian finches are pink and naked until about 12 days old when the beginnings of feathers start to appear. Very young birds also have blue, shiny structures on the sides of their beaks to help their parents see them in the dark.
Diet / Feeding
Natural Diet: Like other finches, Gouldian Finches are seed eaters. During the bird’s breeding season, Gouldian Finches feed mostly on ripe or half-ripe grass seeds of Sorghum Spc.
During the dry season, they forage on the ground for fallen seed.
During the wet season, Spinifex grass seed is an important component of their diet. So far Gouldians have been recorded as consuming 6 different species of grass seed.
Captive Diet: Gouldian Finches should be provided good quality finch food as well as soft foods, fresh water every day, a cuttlebone, as well as vitamins.
The blue-blacked variety cannot produce their vitamin A; and therefore, they especially need vitamins in their soft food. Grit and cuttlebone are important components of a finch’s diet
Alternate (Global) Names
Chinese: ???? … Czech: Amada / Amadina Gouldové … Danish: Gouldsamadine … Dutch: Goulds Amadine / Amandine … Estonian: Ehisamadiin … Finnish: Harlekiinipeippo … French: Diamant de Gould … German: Gouldamadine … Italian: Diamante di Gould … Japanese: Kokinchou … Lithuanian: Guldo kikilis … Norwegian: Gouldamadin … Polish: Amadyna wspania?a … Russian: ??????? ??????, ???????? ??????? … Slovak: Amada pestrá … Spanish: Diamante / de Gould … Swedish: Gouldsamadin
Life Cycle
Gouldian Finches reach reproductive maturity before they are one year old. They generally survive 5 or more years in the wild. Well-cared-for captive birds are reported to live up to 9 years.
Further Finch Reading
- Finch Information
- Index of Finch Species
- Photos of the Different Finch Species for Identification
- Common Health Problems of Finches
- Finch / Canary Diet / Nutrition